

The DAPG biosynthetic genes, phlACBDE, are organized as an operon.

The DAPG synthesis is influenced by edaphic parameters (e.g., pH, mineral concentrations and clay quality), host genotype, host age, pathogen infection, genetic instability of inoculants, and is inhibited by certain pathogen toxins. It has a wide range activity against bacteria, fungi, and helminths. fluorescens strains that occur in natural disease suppressive soils. DAPG is widely distributed in antagonistic P. For both strains, one of the most important is the polyketide antimicrobial compound 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol (DAPG). Strain CHA0 also produces salicylic acid and the polyketide antimicrobial compound, pyoluteorin. fluorescens CHA0 and Q2–87 produce various secondary metabolites with antimicrobial activity, including hydrogen cyanide and metal-chelating siderophores. These organisms have distinct mechanisms in biocontrol and distinct regulation of key biocontrol genes. Well-characterized model strains of each organism were used. The objective of this study was to determine in vitro the impact of two of the most studied biocontrol organisms, Pseudomonas fluorescens and Trichoderma atroviride, on the expression of each other's primary biocontrol genes. Surprisingly, little is currently known at the molecular level about interactions between co-inoculated biocontrol strains despite the level of interest in strain mixtures. An important prerequisite for designing effective strain mixtures is choosing strains that complement rather than interfere with the antagonistic activity of each antagonist. There are, however, other reports of biocontrol strain combinations that had no effect on efficacy or even reduced the level of disease suppressive activity of individual antagonists. Strain mixtures have indeed proven in some cases to be more effective than single strain treatments against a variety of plant diseases. Introduction of two or more antagonists in a strain mixture has been proposed as an approach to improve the level and reliability of biocontrol treatments across an expanded broader range of environments. Pseudomonas, Trichoderma, Biocontrol strain combination, Gene expression, 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol, Chitinase 1 Introduction These results indicate that negative and positive effects on expression of key biocontrol genes may occur while mixing antagonists. fluorescens enhanced phlA expression transiently during growth. atroviride P1 culture filtrates to growing cultures of P. fluorescens CHA0 repressed expression of both Trichoderma chitinases. We found that DAPG enhanced nag1, but not ech42 expression, whereas an unidentified substance from P.
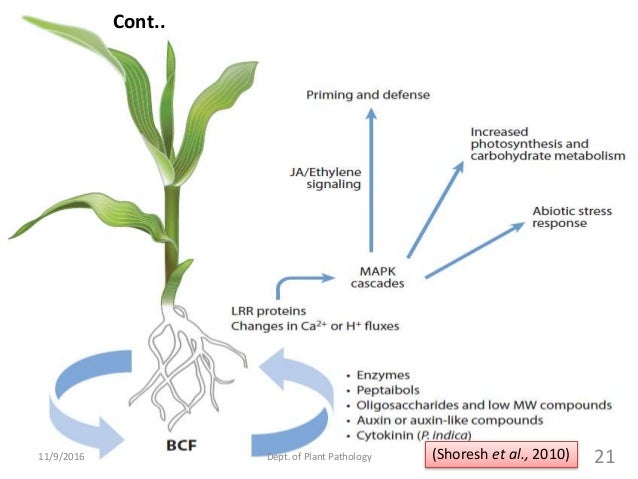
fluorescens CHA0 and ech42-goxA or nag1-goxA fusions in T. Interactions were monitored using the reporter gene constructs, phlA'-'lacZ translational fusion in P.

fluorescens strains CHA0 and Q2–87 and chitinase-producing T. We examined the molecular interactions between the DAPG-producing P. Production of chitinases, such as the ECH42 endochitinase and the NAG1 N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase, is a primary mechanism of action for T. fluorescens strains is the synthesis of 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol (DAPG). One key factor for the biocontrol efficacy of several P. Certain Pseudomonas and Trichoderma strains belong to the most common studied biocontrol agents. The use of bacterial and fungal strain mixtures is a promising way to improve efficacy of biocontrol treatments.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
